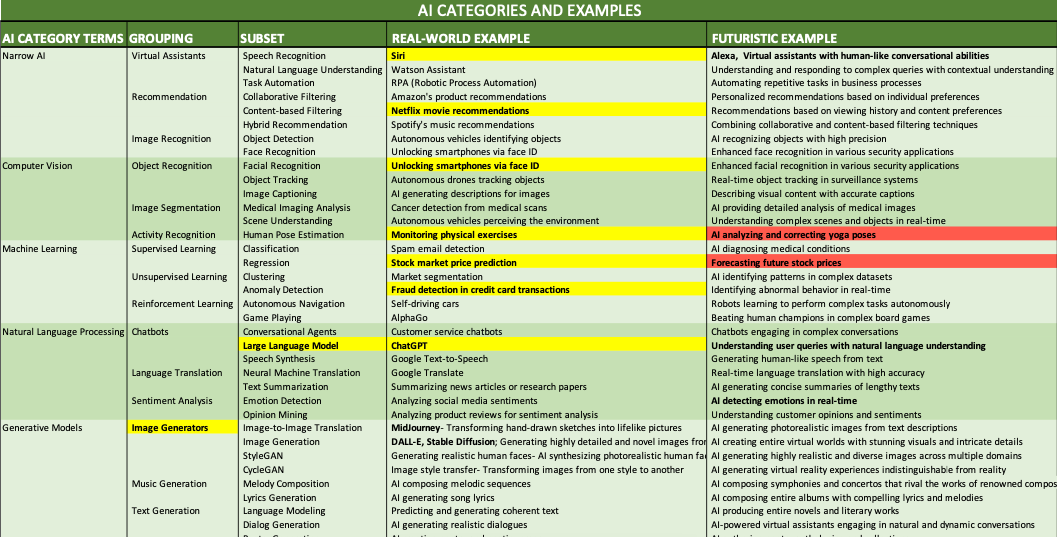
8 AI Terms You Should Know
SUZANNE MCCLENDON • June 14, 2023
Common terms to know

- Chatbot: a computer program designed to simulate human conversation. It uses artificial intelligence techniques to understand and respond to user queries or prompts. For example, a chatbot on a website can help users find information, answer questions, or provide customer support.
- Prompt: a specific input given to an AI model to generate a desired response. It can be a question, statement, or incomplete sentence that sets the context for the AI model to generate a relevant output. For instance, a prompt for an AI language model could be "Translate the following sentence into French: 'Hello, how are you?'"
- Prompt Engineer: a person who specializes in crafting effective prompts for AI models. They have the expertise to design prompts that generate accurate and desired responses from the AI system. A prompt engineer understands the nuances of language and formulates prompts that yield the desired information. They often fine-tune and iterate the prompts to improve the AI model's performance.
- Generative AI: Generative AI refers to the ability of an AI system to generate original and creative content, such as text, images, or music. It involves training AI models to learn patterns and generate new outputs based on the provided input. For example, a generative AI model can create unique paintings or compose music pieces that resemble the style of a specific artist.
- LLM: "Large Language Model" - a type of AI model that has been trained on a vast amount of textual data to understand and generate human-like language. LLMs, such as OpenAI's GPT-3, are capable of performing various language-related tasks, including translation, summarization, and answering questions based on the given context.
- NLP: NLP stands "Natural Language Processing." It is a branch of AI that focuses on enabling computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. NLP algorithms analyze and process text or speech data to extract meaning, recognize entities, determine sentiment, and perform other language-related tasks. Examples of NLP applications include chatbots, language translation, and sentiment analysis.
- Machine Learning
:a subset of AI that involves training algorithms to learn patterns and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. It is achieved by providing the algorithm with large amounts of data and allowing it to learn from the patterns within the data. For example, a machine learning model can be trained on a dataset of emails to classify them as spam or legitimate based on their features.
- Hallucinations: In the context of AI, hallucinations refer to instances when a generative AI model produces outputs that are incorrect, nonsensical, or unrelated to the given context. Hallucinations can occur when the AI model is pushed beyond the limits of its training data or encounters ambiguous or unusual prompts. For example, a language model might generate sentences that are grammatically correct but lack coherence or factual accuracy, resulting in hallucinations.